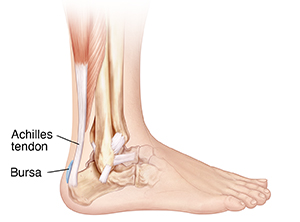
Subcutaneous calcaneal bursitis is a condition that causes heel pain. This pain radiates from the bursa located between your Achilles tendon and skin. A bursa is a fluid-filled sac. Your body has many of them. They are found in areas where rubbing may occur, such as between tendons and bones. The fluid inside them helps ease friction during movement. If they become injured or irritated, you may feel pain.
How to say it
sub-kyoo-TAY-nee-us kal-KAY-neel bur-SI-tis
What causes subcutaneous calcaneal bursitis?
This type of bursitis is mainly caused by wearing shoes that don’t fit correctly. Tight-fitting shoes that rub the back of the heel can irritate the bursa. Women who wear high-heeled shoes are most at risk for this condition. Athletes who wear ill-fitting shoes may also suffer from it.
Symptoms of subcutaneous calcaneal bursitis
Pain and swelling in the heel are typical symptoms. You may also notice redness. Certain shoes, such as tight-fitting ones, may be painful to wear.
Treatment for subcutaneous calcaneal bursitis
The aim of treatment is to ease symptoms so that the bursa has time to heal. Treatment choices include:
-
Rest. You may need to alter or limit activities that cause heel pain. These include high-impact activities like running.
-
Over-the-counter medicine. This helps reduce pain and swelling. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are the most common medicines used. Medicines may be prescribed or bought over-the-counter. They may be given as pills. Or they may be applied to the skin as a gel, cream, or patch.
-
Cold or heat packs. Putting ice or a heating pad or pack on the heel may ease pain.
-
Shoe inserts or padding. Devices such as heel cups or pads for the back of the heel can ease discomfort when moving.
-
Footwear. Don't wear tight-fitting shoes or those that rub the back of the heel. Shoes with an open-back heel, such as clogs, may help.
-
Stretching exercises. Gentle stretching movements can restore range of motion in the ankle and foot. They can also help with pain.
When to contact your doctor
Contact your doctor right away if you have any of these:
-
Fever of 100.4°F (38°C) or higher, or as directed
-
Chills
-
Pain that gets worse
-
Symptoms that don’t get better, or get worse
-
New symptoms
Author: Semko, Laura
© 2000-2025 The StayWell Company, LLC. All rights reserved. This information is not intended as a substitute for professional medical care. Always follow your healthcare professional's instructions.